Moderation of Google Reviews in a nutshell
How can companies with multiple locations improve managing reviews in Google My Business?
Introduction.
According to a report by BrightLocal, as many as 87% of consumers read online reviews when looking for local businesses. At the same time, only half of the respondents would consider supporting a company with a rating lower than four stars.
Moreover, 97% of consumers who read reviews also read businesses’ responses to these reviews, whether positive or negative, which shows the degree of influence that client feedback and brand reactions have on purchasing decisions. Another crucial aspect of the client reviews published online is their feedback on the company’s products or services. Based on this valuable information, businesses can improve their product or service portfolios and decide which of their advantages are worth highlighting further in company marketing communications.
The above statistics confirm the relevance of appropriate communication between the brand and the clients. Fortunately, tools such as Google My Business have considerably reduced the distance between the two parties, and clients can share an opinion about a company seconds after using its services.
Part 1.
The significance of customer reviews for your business
Google search is often the first place people go to look for the items and services they need – and GMB listings are likely to be the first tidbit nugget of information they find. This relates especially to businesses that have physical locations.
However, increasing your business’ discoverability in Google search isn’t the only benefit that comes with putting some work into Google My Business listings. What matters even more is that you will likely receive customer reviews under your business listings. This is one of the best sources of feedback from your customers that can help you improve your strategy and customer service.
If you carefully read and analyze your Google reviews, you may start to understand your customers’ pain points and needs better. And then, you will be able to develop insights-driven solutions to improve your services and strategy to better suit the market’s demands. In turn, it will likely not only make your existing clients more loyal but also help draw the attention of many new ones.
Read and analyze all Google reviews from one dashboard. ➞
Impact of Google Reviews on customer decision making.
Your business’ reviews allow Google to verify whether all of the other online information about your business is actually true. This means that Google can avoid sending its users to businesses that are bogus or unreliable.
But these are not the only reviews Google cares about. It will scour the Internet for reviews on other sites where people search for opinions: Facebook, Yelp, your website and more. This is not surprising if we look at the Local Consumer Review Survey conducted in 2020 by BrightLocal.
According to this report, 87% of consumers read online reviews for local businesses. 60% did so “always” or “regularly”. Moreover, only 48% of consumers would consider using a business with fewer than 4 stars (and bear in mind that a star rating is a paramount review factor).
The conclusion coming from this report is clear – you have to make sure your Google profile has as many reviews as possible (at least 10, to be exact) and ensure that most of them are positive. This way, you will gain trust among potential customers, and they will be more eager to contact or visit your company.
Reply to customers from one place. ➞
Interaction is the key to successful digital marketing.
Listening to your customers is essential, but probably the most valuable feature of Google Reviews is the opportunity to interact with them by responding to their opinions.
Establishing a dialog with your clients will make them feel important and show that you are listening to what they say. Making it clear to customers that you care about their views and feelings is one of the best ways of building their loyalty towards your brand.
This customer care practice may not always be easy as not all the reviews customers share online are positive. But there’s no need to panic if you receive some less-than-perfect reviews – it’s just part of business. Negative reviews can actually benefit your online image if you respond to them in an appropriate way.
Besides, another great thing about customer reviews is that they are a free source of intel about your services. Thanks to them, you can possibly get some great ideas as to how you should improve your business, without the hassle of thorough market research. Don’t underestimate your customers’ ideas as, after all, they’re the ones who have real experience with what you sell.
Important factors influencing your SEO.
Google reviews significantly impact your Google business rating and increase your online exposure. Done right, Google Reviews will increase your visibility by boosting your SEO. Just take a look at some facts:
Local pack.
Google’s Local Pack is a list of the top three businesses relevant to a search query, presented under the map at the top of the local search results page.
Reviews determine 13% of your business’s chance of ranking in Google’s Local Pack, while your Google My Business (which places you in Maps) accounts for 19%.
Also, it’s good to know that review stars can boost CTR by as much as 35%. That might not sound deal-breakingly significant, but it makes them more impactful than your citation (mentions of your business online), behavioral (bounce rate, time-on-page, etc.) and social (social media) signals.
Localized organic ranking.
Reviews are also important factors in localized organic ranking, even if the effect is slightly less than for the Local Pack. Localized organic ranking is the same as non-localized (or generalized, i.e. everything on the Internet, local or not) search results.
The quantity, diversity, quality, etc. of your reviews and your My Business signals (including Maps) determine a total of 14% each of your localized ranking. Which, again, means they carry more weight than social signals.
| MAIN BENEFITS OF GOOGLE REVIEWS | |
|---|---|
| HIGHER RANKING ON GOOGLE | The more 5-star ratings a company has, the better its perception among consumers. This, in turn, has a direct impact on its search result ranking. Also, review stars can boost CTR by as much as 35%. |
| BETTER CLIENT AND COMPANY AWARENESS | Client reviews reflect consumer shopping experiences, providing the company with an outside-in perspective. This can help identify the organization’s strengths and weaknesses procedures for improvement (e.g. complaint handling process). On this basis, the company can introduce the necessary changes that will eventually contribute to its development. |
| ENHANCED QUALITY OF CUSTOMER SERVICE | Seamless moderation of client reviews and a proactive approach to solving customer problems translate directly into a more positive evaluation of the company’s customer service standards. This, in turn, may lead to increased sales because a happy client will not only make a return purchase but will also recommend the company to their friends. |
Part 2.
Best practices when managing Google Reviews
Interaction is the key to successful digital marketing.
Listening to your customers is essential, but probably the most valuable feature of Google Reviews is the opportunity to interact with them by responding to their opinions.
The quantity, diversity, quality, etc. of your reviews and your My Business signals (including Maps) determine a total of 14% each of your localized ranking. Which, again, means they carry more weight than social signals.
Since reviews and ratings can help in terms of online visibility, your exposure without them might be fairly poor. But how do you get your first reviews? If you provide excellent service to your customers, quite frankly, all you need to do is ask. When the process starts, you’ll start gaining momentum. Once ratings start coming in, you’ll probably get more and more recognition.
Deliver personal experience.
Handling Google Reviews might take a chunk of your time, but the results make your efforts worthwhile.
Responding to reviews builds credibility, with customers and with Google itself. Answering reviews gives you a chance to show your customers that you value their feedback. Even in the case of negative reviews, a friendly, considerate answer also has the power to change the unhappy customer’s sentiment. Think about it as a question-and-answer situation. Google reviews allow you to respond, acknowledge, and humanize the entire experience. And the beauty of it is that there’s no technical option to start a long conversation thread. It’s simple – review and answer, that’s it!
However, the author can still edit their rating, so if you get some harsh critique, your reaction might show you in a better light if you play it right.
Easily respond to reviews to build credibility. ➞
The more you customize your replies, the better – you don’t want to make your customers feel like they have had a robot reply, while they took time to write a genuine opinion.
So even if you are just thanking a customer for a positive opinion, try to make it personal.
Learn to love negative reviews.
Unfortunately, even the best businesses with fantastic customer service get negative reviews. But with a few smart moves (which include keeping your cool), you can address the unsatisfied and turn the situation around.
The first thing you want to do is recognize an actual negative review. One that contains a relevant opinion and expresses feelings related to a customer’s experience. Something sincere that you can respond to. This might be a great opportunity to show the community that you really care, and to express your concern, showing that customers are always the top priority to you
If clients add negative reviews on your listing, make sure to provide a reply, explaining the situation and trying to compensate for any inconvenience caused. This might increase the chances of the clients changing their mind and raising their ratings.
Reply in a way that shows you take their opinion seriously and that you’re interested to know the details of what exactly went wrong. Reaching out to customers by replying to reviews (good and bad) can be a strong addition to your online image. It’s not only a way to protect your brand, but it can also be a very direct and human aspect of your marketing, customer service, and social media strategy. The more reviews you have, the better. Too few means customers will overlook your business in favor of those with more opinions. If you’re not getting enough Google reviews, encourage customers to write them. As many as 77% of customers say they are happy to leave a Google Review when asked, says Podium’s survey.
And responding to these reviews is just as important as getting them. Giving reviewers feedback is highly encouraged by Google. It also means that you are actively engaged in delivering a great customer experience. Even replying with a brief thank you for each positive Google Review can boost your SEO. It also allows you to use some of your keywords.
Part 3.
How to Manage Google Reviews for Multiple Business Locations
Google Reviews Moderation.
Google reviews are a great source of recommendations from satisfied customers, but things can go very wrong if someone has an unpleasant experience (and someone eventually will.) A social media moderator’s job is also moderating these reviews – and with multiple locations, this channel alone can consume hours of their time.
Goals of reviews moderation
- Engaging in conversations with your audience
- Building relationships with your potential and existing customers
- Helping build consistent brand communication
- Increasing your brand reach and boosting traffic to your website
- Encouraging customers to create user-generated content, one of the best ways to engage your audience
- Saving your brand reputation by reacting quickly to inappropriate content or angry customer complaints
- Deleting or hiding inappropriate content, competitors’ links, or abusive comments
- Playing a crucial part in your customer service and your overall customer experience
- Moving your customers through your sales funnel and often helping to sell your products and services
- Letting you know when there’s a need for an immediate reaction like poor customer service in a specific location

Managing multiple locations on Google is time-consuming.
Growing a chain business and managing multiple locations often creates the necessity to set up multiple business listings to build visibility on Google Maps and in Google Search.
And the simple math is that the more business locations you own, the more reviews and customer inquiries you can expect. At some point, this can become overwhelming.
You can manage multiple locations from the Google My Business panel, but you’ll still have to switch between them to answer reviews. Responding to all the reviews that appear under numerous listings can be inconvenient for a few reasons:
- It requires frequent manually checking if any new reviews were added
- Each reply would have to be typed out manually from the particular account
All these factors could negatively affect the quality of your customer service. If you get many reviews every day under each of your listings, you might start to miss some of them. This might not seem like a big problem at first but can eventually turn into a crisis if things spiral out of your control. After all, no one likes to be ignored, right?
Managing Google Reviews manually is not only time-consuming. Hopping between different locations might leave space for mistakes. As a result, in the long run, it can also reduce your customers’ overall satisfaction when dealing with your business. Luckily, there are ways to streamline the process and effectively interact with customer reviews.
One tool to manage multiple Google My Business accounts.
Dedicated solutions like NapoleonCat allow you to link multiple profiles and accounts – and manage them all from one simple dashboard. Using the Social Inbox can reduce that time many times over.
Like in the case of CCC, a popular European footwear retaile and producer, which – with around 500 locations and 1000-1500 Google reviews a month – reduced time spent on moderation to just 1-1.5 hours, 3-4 times a week.
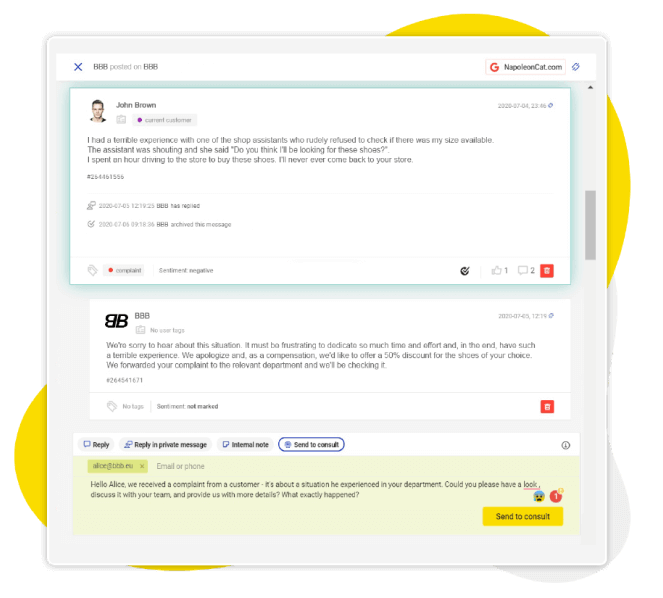
Having the ability to view and manage all Google Reviews in one stream, regardless of the locations they were added to, makes the whole processalmost effortless.
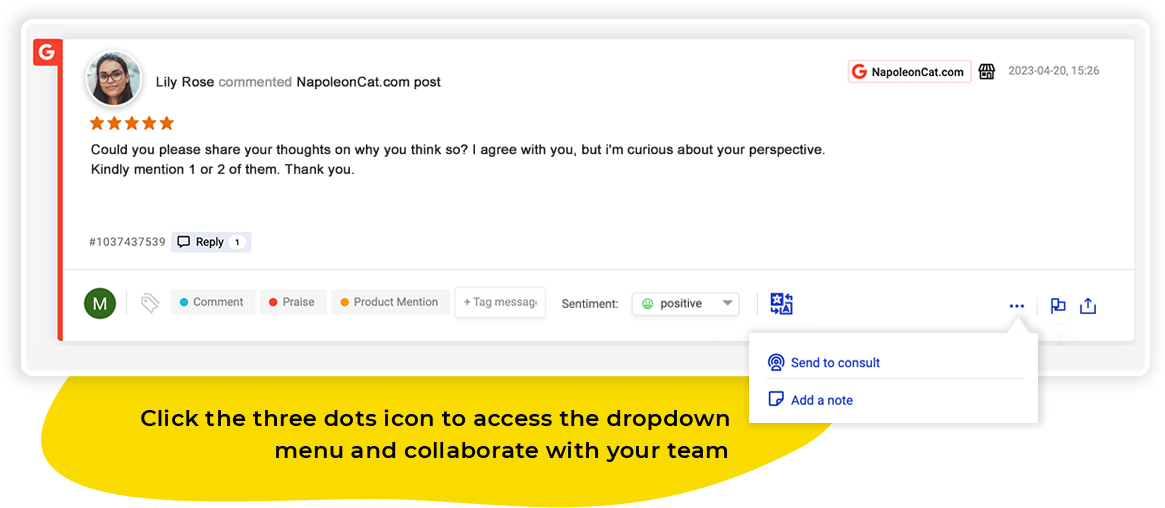
NapoleonCat’s Social Inbox allows you to link all of your Google My Business accounts to one easy-to-use control panel and manage all the reviews from one dashboard.
Using the Social Inbox, you can easily respond to any review that shows up under your listings – reviews from all connected accounts will automatically show up in the dashboard. To answer a review, simply choose the ‘Reply’ option in the lower right corner of each individual ticket
Once you get familiar with replying via Social Inbox, you can also create replytemplates – or what we call ‘saved replies’ – to speed up the process of addressing generic reviews. It is best to create a couple of them for both positive and negative reviews, to be prepared for more scenarios – and to add more character to your replies.

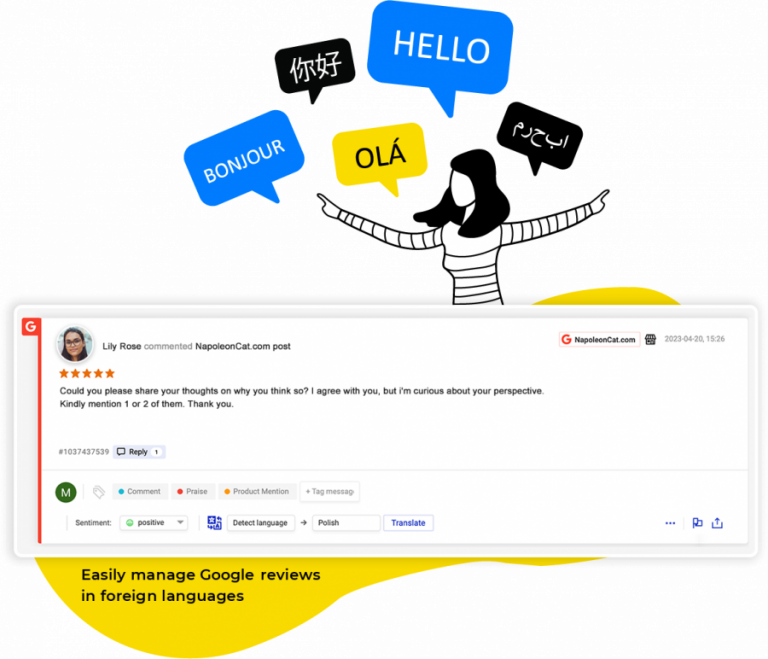
If you receive Google reviews in foreign languages, you can easily manage those reviews with our built-in Translations feature.
You can translate reviews and reply to them in over 100 languages that are supported by Google Translate. The foreign language included in the review is automaticallydetected by NapoleonCat, but you can always change it.
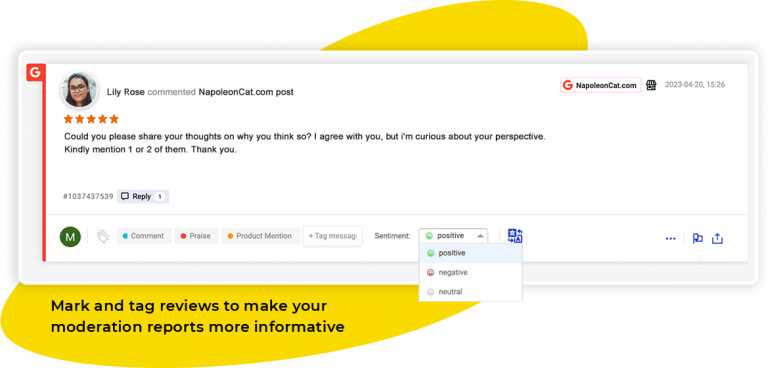
Another useful feature of the Social Inbox is the ability to assign sentiment to every review.
Every message can be tagged as positive, negative, or neutral. You can also set your own tags in Project Settings in NapoleonCat (left-side menu).
Doing this will make it easier for you to sort reviews based on the attitude towards your company.
- complaint
- irrelevant
- spam
- praise
As for teamwork, we should add that the Social Inbox truly caters o social media and customer service teams. Each review is a ticket that can be assigned to a team member or sent to a supervisor or stakeholder with a request for help or consultation.
Internal notes can be added to make sure that everyone has all the information they need to handle each and every review with ease.
Moderation of Google Reviews is a story that never ends.
Managing multiple Google business profiles takes a greatdeal of work. If you own a chain of restaurants, shops,or service points, manually managing a high volumeof reviews may prove to be impossible.
That’s why the best way to ensure that your customer relations remain in good shape regardless of your company’s size is to streamline the process and save time using the dedicated tool.
73% of surveyed customers said that a review should be placed within the past month if it’s to impact their decision. 50% said it ought to be placed within the past two weeks!
Moreover, you must remember that customers want to read recent reviews, and they’re usually not interested in how your company performed last year, let alone several years ago.
This means that getting more Google reviews is not a one-time goal. You should make it a long-term priority and implement solutions that will allow you to get more reviews on Google in the coming weeks and months. Thankfully, we have a strategy that might just do the trick!
Social Inbox delivers you one comprehensive dashboard that combines all of your Google My Business profiles and locations in one place. This way, you can quickly check new reviews and reply to them. The consolidation of many stores and comments in one view is a convenient solution that enables you to spot your strengths and areas that need improvement.
MANAGE ALL SOCIAL MEDIA FROM ONE PLACE.
COMMENTS, MESSAGES, REVIEWS